Using the Jenkins Pipeline Stage with Spinnaker
You can launch Jenkins jobs to run Liquibase and perform database updates in a Spinnaker while using a Jenkins pipeline stage.
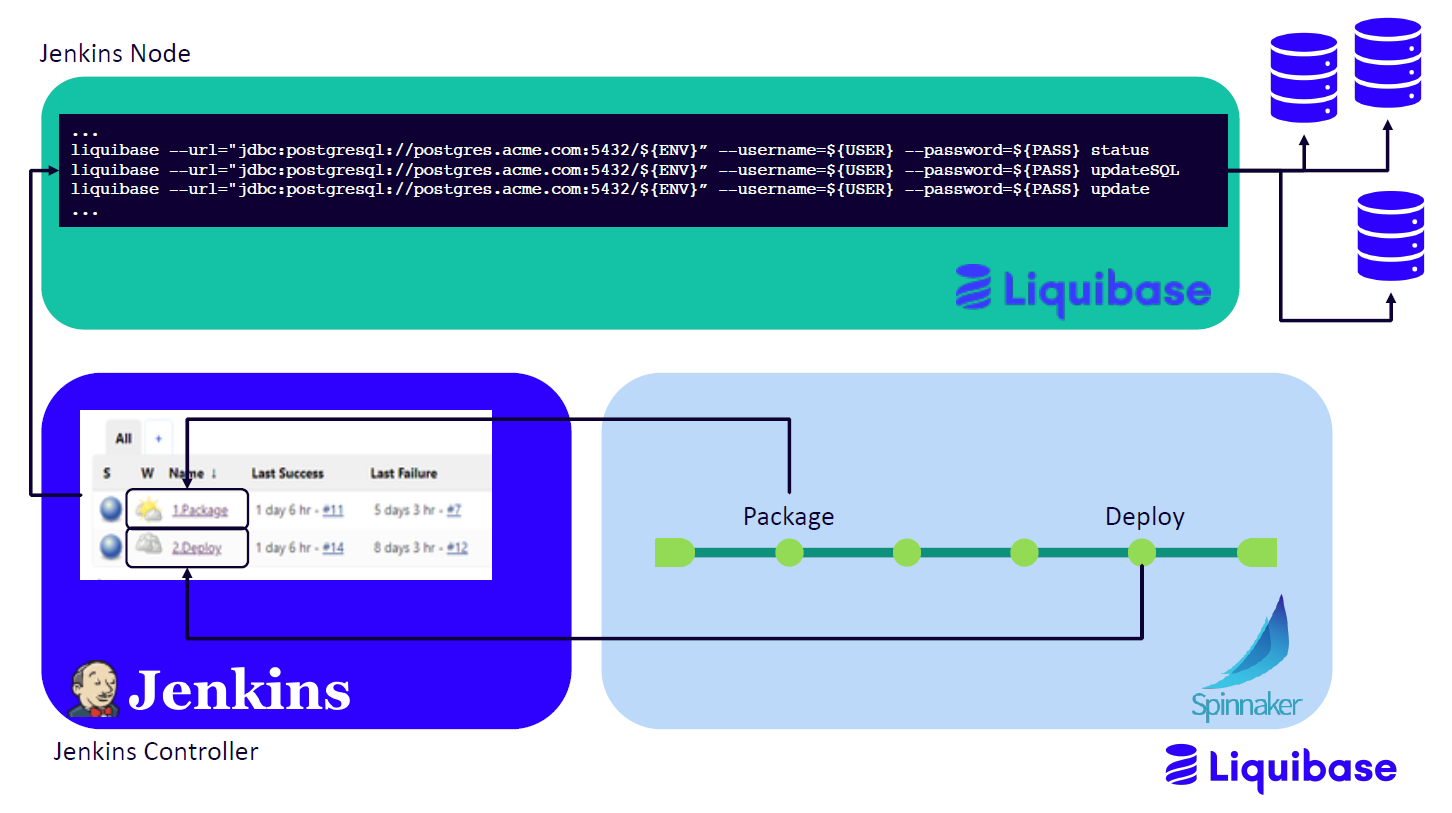
The following diagram shows the Jenkins pipeline stage calling a Jenkins job which executes Liquibase commands on a Jenkins subordinate.
Note
The procedure mentioned in this documentation has been built on top of the application created in the Jenkins article.
Setting up Spinnaker and the Jenkins pipeline stage
To configure Jenkins and Spinnaker, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install Jenkins and Spinnaker
Make sure you set up Jenkins and Spinnaker.
Step 2: Configure Jenkins
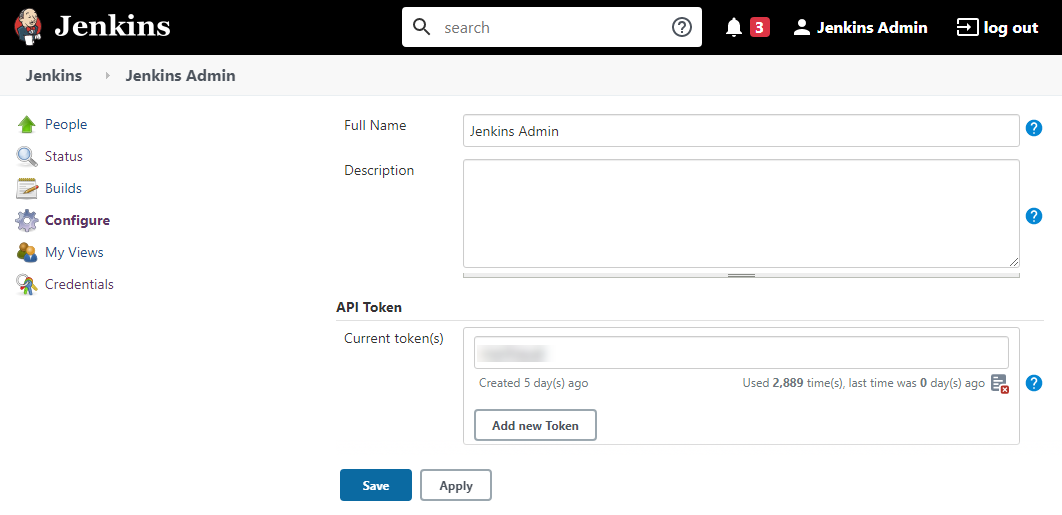
Configure a Jenkins master node using the API Token:
-
Go to your Jenkins instance and select Configure.
Note
If you are new to Jenkins, see Jenkins Documentation.
-
Enter a full name, description, and API Token that you want to add:
-
Select Save.
Step 3: Setup Package and Deploy Jobs in Spinnaker
Deploy package and deploy jobs pre-configured so that Spinnaker can run those jobs.
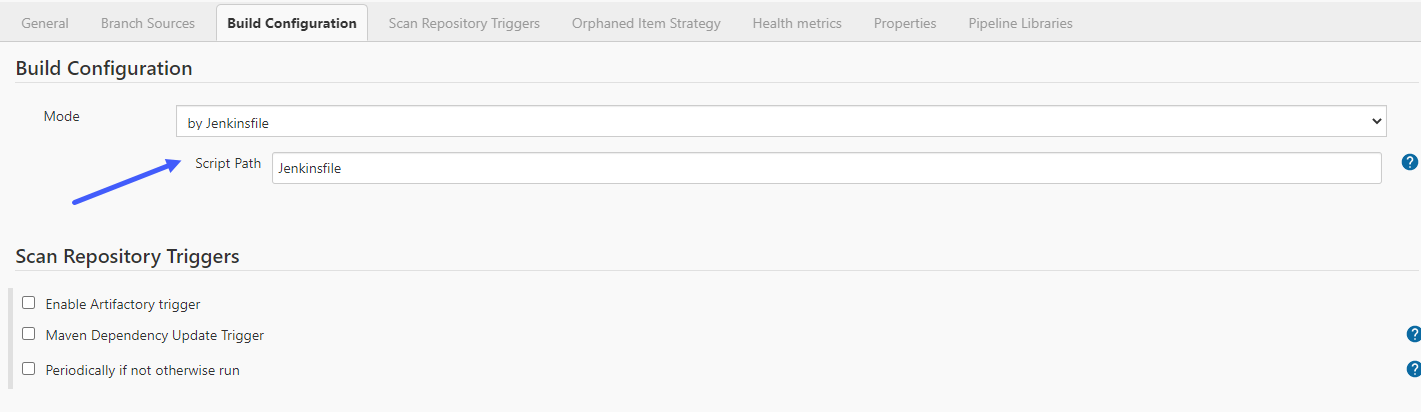
To deploy jobs, use examples of the [Jenkinsfile](https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/pipeline/jenkinsfile/) provided later in this documentation. After creating your Jenkinsfile and starting to configure a build, specify mode as a Jenkinsfile and enter the path to this file. The following example shows the path to a Jenkinsfile pointing to the root of the repository.
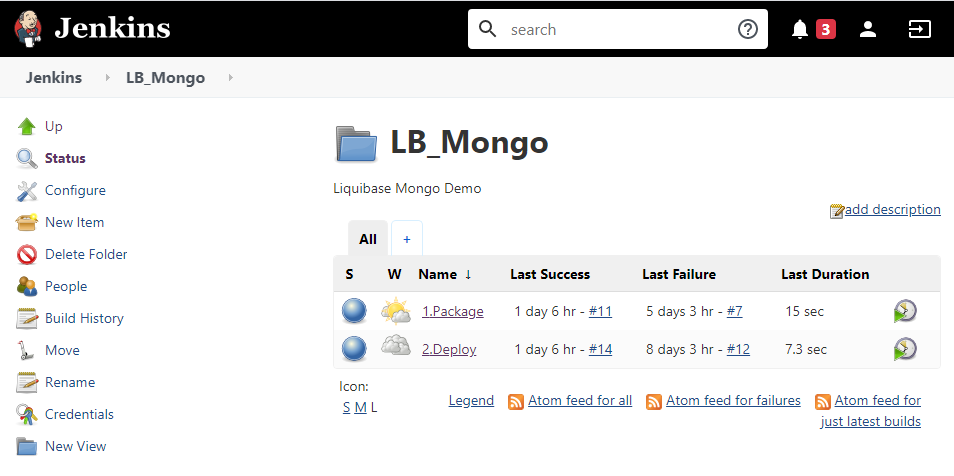
Package operation
The package pipeline stage deploys changes to the DEV environment and produces a versioned artifact. The package job in Jenkins accepts three parameters – USERNAME, PASSWORD, and ENV:
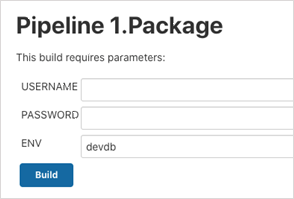
The pseudo-code looks like this:
- Perform pre-check to ensure all tooling is installed and obtain the needed information about each tool’s version
- Check out a branch from a Git repository
- Deploy code to DEV database
- Create a versioned artifact
The following is an example of the Jenkinsfile to package Liquibase changeset:
```
#!/usr/bin/env groovy
// Packager declarative pipeline
//
pipeline {
agent {
node {
label 'datical'
customWorkspace "/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/LB_mongo/1.Package-${BUILD_NUMBER}/"
}
}
environment {
GITURL="git@github.com:datical-customersuccess"
PROJ_REPO="LB_mongo"
PATH="$PATH:/opt/liquibase/lb_4.00"
}
stages {
stage ('Precheck') {
steps {
sh '''
ls -alh
pwd
whoami
which git
git --version
liquibase --version
git config --global user.email "jenkins@datical.com"
git config --global user.name "jenkins"
'''
} // steps
} // stage 'precheck'
stage ('Checkout') {
steps {
// checkout Liquibase project from Repo
checkout([
$class: 'GitSCM',
branches: [[name: '*/master']],
doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false,
extensions: [
[$class: 'RelativeTargetDirectory', relativeTargetDir: "${PROJ_REPO}"],
[$class: 'LocalBranch', localBranch: 'master']],
submoduleCfg: [],
userRemoteConfigs: [[url: "${GITURL}/${PROJ_REPO}.git"]]
])
} // steps for checkout stages
} // stage 'checkout'
stage ('Branches'){
steps {
sh '''
#{ set +x; } 2>/dev/null
cd ${PROJ_REPO}
echo "Current Directory:" `pwd`
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/main main
git status
'''
} // steps
} // Branches stage
stage('Package SQL') {
steps {
sh '''
#{ set +x; } 2>/dev/null
echo "==== Running PackageSQL (using Liquibase::update) ===="
cd ${PROJ_REPO}
liquibase --url=mongodb://localhost:27017/${ENV} \
--username=${USERNAME} \
--password=${PASSWORD} \
--log-level=info \
update
'''
} // steps ...
} // stage 'Package SQL'
stage('Artifact') {
steps {
sh '''
#{ set +x; } 2>/dev/null
echo
echo "==== Creating ${BUILD_NUMBER}.zip ===="
zip -q -r ${BUILD_NUMBER}.zip *
#mv *.zip ..
echo
echo "=====FINISHED===="
'''
// upload artifacts to Artifactory
script {
def server = Artifactory.server 'ArtifactoryServer'
def uploadSpec = """{
"files": [
{
"pattern": "*.zip",
"target": "${REPOSITORY_BASE}/${BRANCH}/database/",
"flat" : "false"
}
]
}"""
server.upload(uploadSpec)
} // steps for Artifact
} // stage artifact
} // stages
post {
always {
//archiveArtifacts "**/daticaldb.log, **/Reports/**, **/Logs/**, **/Snapshots/**"
sh '''
ls -alh
'''
}
}
} // pipeline
```
Deploy operation
The deploy pipeline stage pulls down the specific artifact version and deploys it to a target database environment. The deploy job in Jenkins accepts four parameters – USERNAME, PASSWORD, ENV, and ARTIFACT_VERSION:
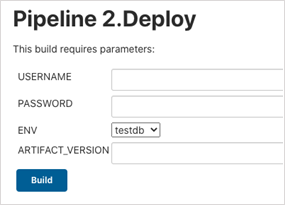
The pseudo-code looks like this:
- Perform pre-check to ensure all tooling is installed and obtain necessary information about each tool’s version
- Check out a specific version of the artifact
- Deploy code to a target database
The following is an example of the Jenkinsfile to deploy a Liquibase change:
```
#!/usr/bin/env groovy
// Deploy declarative pipeline
//
pipeline {
agent {
node {
label 'datical'
customWorkspace "/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/LB_mongo/2.Deploy-${BUILD_NUMBER}/"
}
}
environment {
TARGET_DB="${params.TARGET_DB}"
ARTIFACT_VERSION="${params.ARTIFACT_VERSION}"
PATH="$PATH:/opt/liquibase/lb_4.00"
PROJ_DIR="LB_mongo"
}
stages {
stage ('Precheck') {
steps {
sh '''
ls -alh
pwd
whoami
liquibase --version
'''
} // steps
} // stage 'precheck'
stage('Retrieve Artifact') {
steps {
// download artifact from Artifactory
script {
def server = Artifactory.server 'ArtifactoryServer'
def downloadSpec = """
{
"files": [
{
"target": "${PROJ_DDB}/",
"pattern": "${REPOSITORY_BASE}/${BRANCH}/database/${ARTIFACT_VERSION}.zip",
"explode": "true",
"flat" : "false"
}
]
}
"""
server.download(downloadSpec)
}
} // steps for Artifact
} // stage artifact
stage('Status Check') {
steps {
sh '''
set +x
if [ ${TARGET_DB} == proddb ]
then
cd ${PROJ_DIR}
echo "Checking if changes have been deployed to Test"
if liquibase --url=mongodb://localhost:27017/testdb \
--username=${USERNAME} \
--password=${PASSWORD} \
status | grep -q "is up to date"; then
echo "Changes have been applied"
else
echo "=========== FAILURE! ================="
echo "Changes have not been applied to test"
echo "All changes must be applied to test before Prod"
echo "======================================"
exit 1
fi
fi
'''
} // Steps
} // Status Check
stage('Deploy SQL') {
steps {
sh '''
#{ set +x; } 2>/dev/null
echo
echo "==== Running Deploy (using Liquibase::update) ===="
cd ${PROJ_DIR}
liquibase --url=mongodb://localhost:27017/${${ENV} \
--username=${USERNAME} \
--password=${PASSWORD} \
--log-level=info \
update
'''
} // steps ...
} // stage 'Deploy SQL'
} // stages
post {
always {
// Jenkins Artifacts
//archiveArtifacts "**/daticaldb.log, **/Reports/**, **/Logs/**, **/Snapshots/**"
sh '''
ls -alh
'''
} //always
} // post
} // pipeline
```
Step 4: Apply Jenkins API Token in Spinnaker
# Access Halyard pod
export HAL_POD=$(kubectl -n spinnaker get pod -l app=halyard -oname | cut -d'/' -f 2)
kubectl -n spinnaker exec -it ${HAL_POD} bash
# Halyard command to enable Jenkins
hal config ci jenkins enable
# export environment variables
export BASEURL=http://<jenkinsmaster>.datical.net:8080
export USERNAME=admin
export PASSWORD=<API Token>
hal config ci jenkins master add <name_of_your_jenkins_master> --address $BASEURL --username $USERNAME --password $PASSWORD
# apply changes to Halyard
hal deploy apply
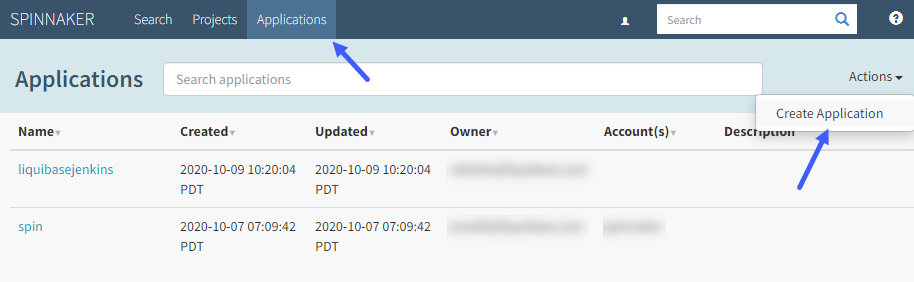
Step 5: Create the Spinnaker Pipeline
In Spinnaker, perform the following:
- Go to Applications, select Actions, and then select Create Application
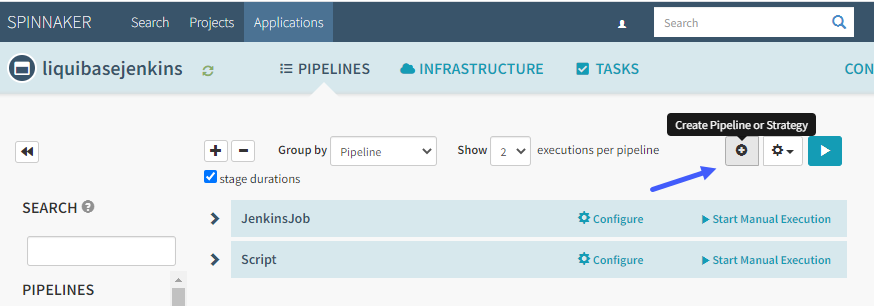
- Select Create Pipeline or Strategy to create a pipeline in the application
-
Configure a Jenkins pipeline stage by adding the following parameters:
-
Controller
- Job
- Property File
- Artifact Version
- Target Database
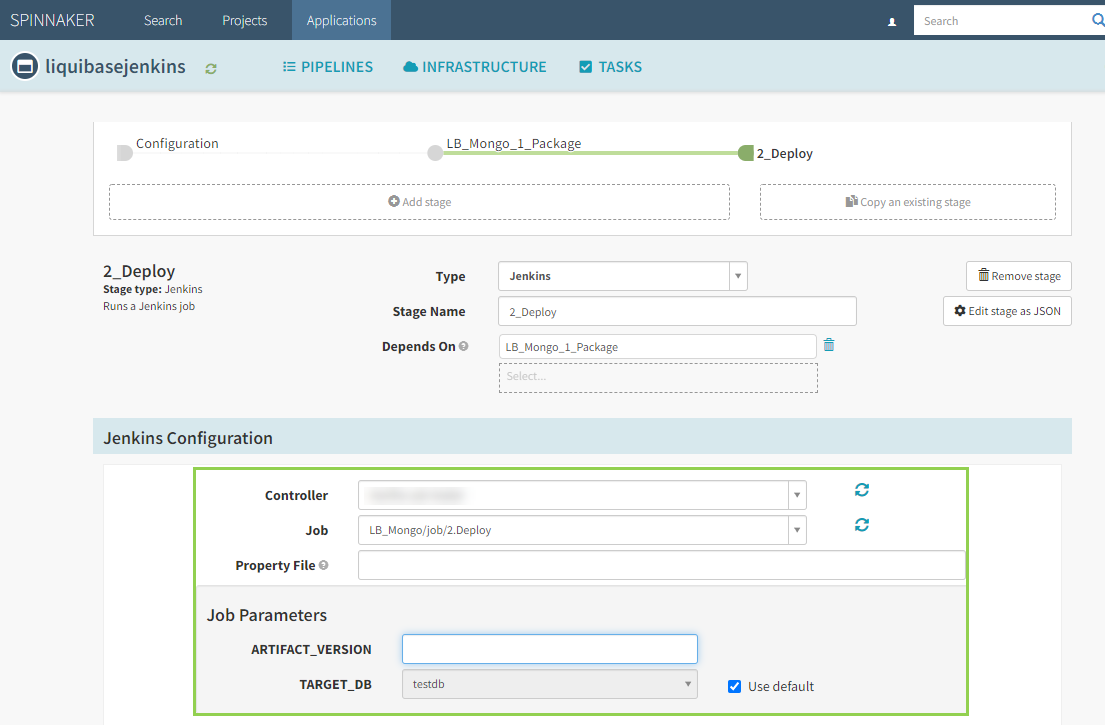
Step 6: Select Start Manual Execution to run the pipeline
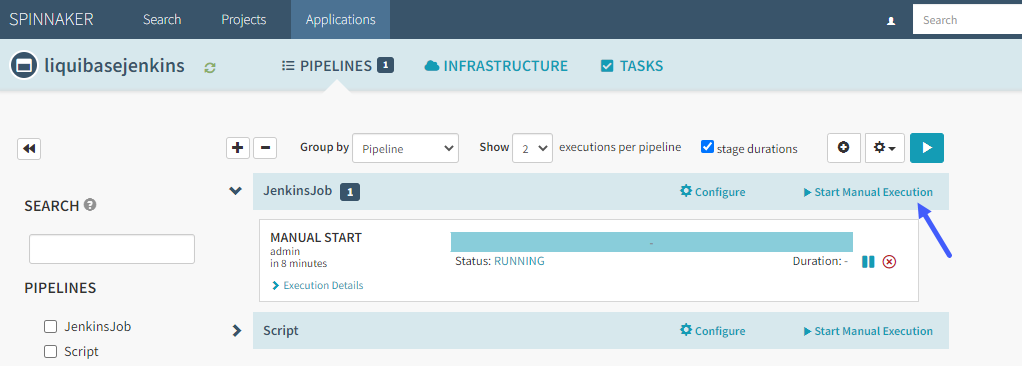
You can confirm an execution of the job by going to Jenkins and viewing the console output.
Using Spinnaker Pipeline as code (JSON)
As all Spinnaker jobs are based on JSON, see JSON for jobs you used if you want to manage your Spinnaker pipeline as a code:
The package pipeline stage:
Input parameters to a Jenkins package job include database credentials (USERNAME and PASSWORD) and the name of the target database (ENV):
"stages": [
{
"continuePipeline": false,
"failPipeline": true,
"job": "LB/job/1.Package",
"master": "jenkins-master",
"name": "LB_1_Package",
"parameters": {
"USERNAME": "lbusername",
"PASSWORD": "lbpassword",
"ENV": "devdb"
},
"refId": "1",
"requisiteStageRefIds": [],
"type": "jenkins"
}
]
The deploy pipeline stage:
Input parameters to a Jenkins deploy job include database credentials (USERNAME and PASSWORD), the name of the target database (ENV), and the artifact version:
"stages": [
{
"continuePipeline": false,
"failPipeline": true,
"job": "LB/job/1.Package",
"master": "jenkins-master",
"name": "LB_2_Deploy",
"parameters": {
"USERNAME": "lbusername",
"PASSWORD": "lbpassword",
"ENV": "proddb",
"ARTIFACT_VERSION": "13"
},
"refId": "2",
"requisiteStageRefIds": [
"1"
],
"type": "jenkins"
}
]
